23. Image transform
23.1. Transform
Use the
Image.transform(size, method, data=None, resample=Resampling.NEAREST, fill=1, fillcolor=None) method returns a transformed image.This method creates a new image with the same mode as the original.
- Image.transform(size, method, data=None, resample=Resampling.NEAREST, fill=1, fillcolor=None)
- size - The output size.method - The transformation method. This is one of:Image.Transform.EXTENT (cut out a rectangular subregion),Image.Transform.QUAD (map a quadrilateral to a rectangle),Image.Transform.AFFINE (affine transform),Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE (perspective transform),Image.Transform.MESH (map a number of source quadrilaterals in one operation).data - the parametrs for the method.resample - Optional resampling filter. It can be one of:Resampling.NEAREST (use nearest neighbour) [if the image has mode “1” or “P”],Resampling.BILINEAR (linear interpolation in a 2x2 environment),Resampling.BICUBIC (cubic spline interpolation in a 4x4 environment).fill - It is unused, unless a class object is used for the method (see docs).fillcolor - Optional fill color for the area outside the transform in the output image.
23.2. Method and Data:
Image.Transform.EXTENT (cut out a rectangular subregion)
A 4-tuple (x0, y0, x1, y1) also known as a bounding box.
Maps a rectangle (defined by two corners) from the image to a rectangle of the given size.
The resulting image will contain data sampled from between the corners, such that (x0, y0) in the input image will end up at (0,0) in the output image, and (x1, y1) at size.
This method can be used to crop, stretch, shrink, or mirror a rectangle in the current image.
Image.Transform.QUAD (map a quadrilateral to a rectangle),
An 8-tuple (x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3) which contain the upper left, lower left, lower right, and upper right corner of the source quadrilateral, moving anticlockwise.
Image.Transform.AFFINE (affine transform),
A 6-tuple (a, b, c, d, e, f) which contain the first two rows from an affine transform matrix.
For each pixel (x, y) in the output image, the new value is taken
from a position (a*x + b*y + c, d*x + e*y + f) in the input image, rounded to the nearest pixel.
This function can be used to scale, translate, rotate, and shear the original image.
Translate xt, yt with [1, 0, xt, 0, 1, yt] e.g. [1, 0, -64, 0, 1, -32]
Mirror with [-1, 0, im.width, 0, 1, 0] e.g. [-1, 0, 256, 0, 1, 0]
Dilate dx, dy with [dx, 0, 0, 0, dy, 0] e.g. [0.5, 0, 0, 0, 0.75, 0]
Shear rx, ry with [1, rx, 0, ry, 1, 0] e.g [1, 0.01, 0, -0.05, 1, 0]
Rotate θ with [cosθ, -sinθ, 0, sinθ, cosθ, 0] e.g. [0.98, -0.17, 0, 0.17, 0.98, 0]
Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE (perspective transform),
The 8 transform coefficients (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h) correspond to the following transformation:
x’ = (ax + by + c) / (gx + hy + 1)
y’ = (dx + ey + f) / (gx + hy + 1)
These 8 coefficients can in general be found from solving 8 linear equations that define how 4 points on the plane transform.
Image.Transform.MESH (map a number of source quadrilaterals in one operation).
A list of (bounding box, quad) tuples.
[((0, 0, w//2, h//2), (0, 0, 0, h, w, h, w, 0)), ((w//2, h//2, w, h), (0, 0, 0, h, w, h, w, 0))]
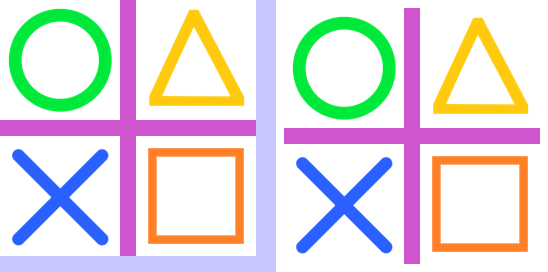
23.3. Transform.EXTENT crop
from PIL import Image
def box_cropped_edges(im, left, top, right, bottom):
w, h = im.size
return (w - left - right, h - top - bottom), (left, top, w - right, h - bottom)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
# crop
new_size, box = box_cropped_edges(im, 8, 8, 8, 8)
im_new = im.transform(new_size, Image.Transform.EXTENT, data=box)
im_new.save("image/transform_extent_box_cropped_edges.png")
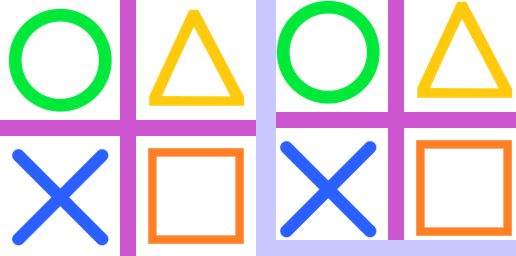
23.4. Transform.EXTENT expand
from PIL import Image
def box_cropped_edges(im, left, top, right, bottom):
w, h = im.size
return (w - left - right, h - top - bottom), (left, top, w - right, h - bottom)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
# expand crop with <0 values
new_size, box = box_cropped_edges(im, -8, -8, -8, -8)
im_new = im.transform(new_size, Image.Transform.EXTENT, data=box)
im_new.save("image/transform_extent_box_expand.png")
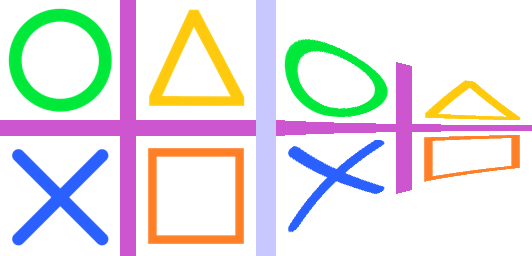
23.5. Transform.QUAD
from PIL import Image
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
quad = [0, 0, 0, 256, 256, 512, 256, -256]
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.QUAD, data=quad)
im_new.save("image/transform_quad.png")
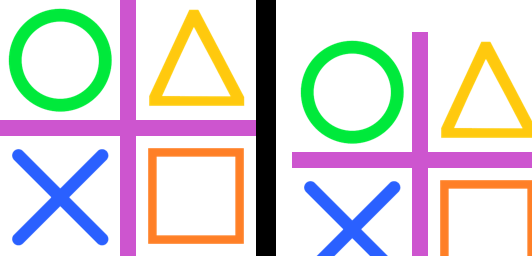
23.6. Transform.AFFINE translate
from PIL import Image
def affine_translate(right=0, down=0):
return (1, 0, -right, 0, 1, -down)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
affine = affine_translate(right=16, down=32)
im_new = im.transform(im.size, Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_translate.png")
23.7. Transform.AFFINE mirror
from PIL import Image
def affine_mirror(im, hor=True, vert=False):
if hor == True and vert == True:
return (-1, 0, im.width, 0, -1, im.height)
elif hor == True:
return (-1, 0, im.width, 0, 1, 0)
elif vert == True:
return (1, 0, 0, 0, -1, im.height)
else:
return (1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
affine = affine_mirror(im, hor=True, vert=False)
im_new = im.transform(im.size, Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_mirrorhor.png")
affine = affine_mirror(im, hor=False, vert=True)
im_new = im.transform(im.size, Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_mirrorvert.png")
affine = affine_mirror(im, hor=True, vert=True)
im_new = im.transform(im.size, Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_mirrorverthor.png")
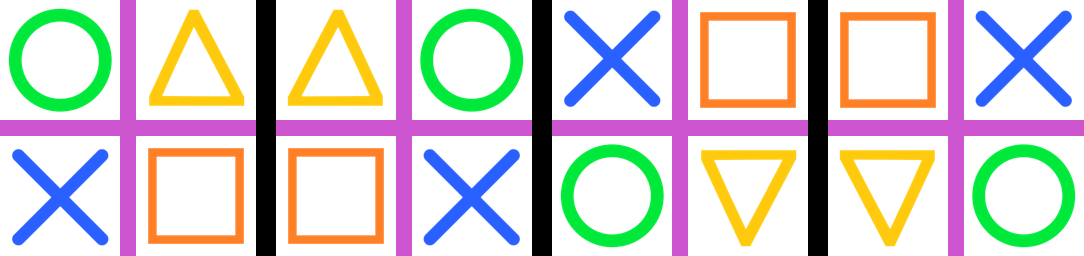
23.8. Transform.AFFINE dilate
from PIL import Image
def affine_dilate(xfactor=1, yfactor=1):
return (1 / xfactor, 0, 0, 0, 1 / yfactor, 0)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
affine = affine_dilate(xfactor=2, yfactor=1)
im_new = im.transform(im.size, Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_dilate.png")
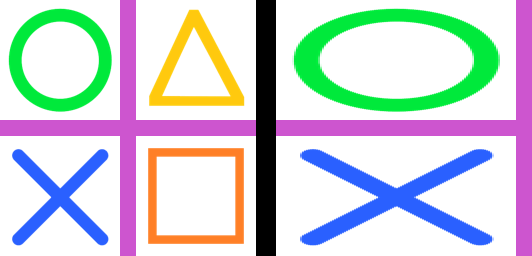
23.9. Transform.AFFINE shear
from PIL import Image
def affine_shear(xpercent=1, ypercent=1):
return (1, xpercent / 100, 0, ypercent / 100, 1, 0)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
affine = affine_shear(xpercent=1, ypercent=-5)
im_new = im.transform(im.size, Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_shear.png")
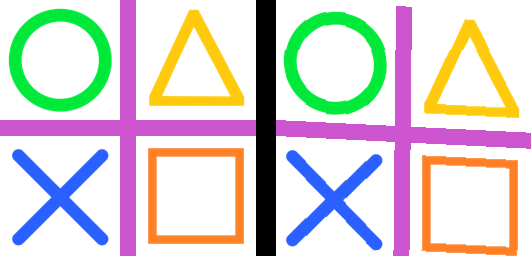
23.10. Transform.AFFINE tilt_hor
from PIL import Image
def affine_tilt_hor(im, theta):
st = round(math.tan(math.radians(theta)), 3)
w = im.width
xshift = abs(st) * w
new_w = w + int(xshift)
affine = (1, st, -xshift if st > 0 else 0, 0, 1, 0)
# print("affine_tilt_hor ", affine)
return new_w, affine
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
new_w, affine = affine_tilt_hor(im, theta=-20)
im_new = im.transform((new_w, im.height), Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_tilt_hor.png")
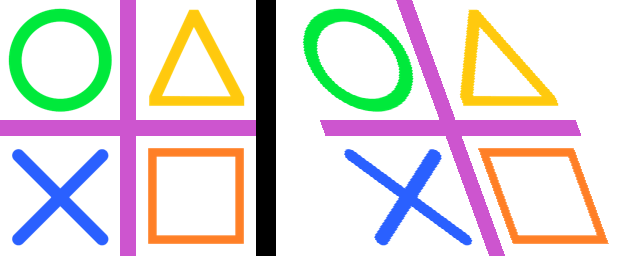
23.11. Transform.AFFINE tilt_vert
from PIL import Image
def affine_tilt_vert(im, theta):
ct = round(math.tan(math.radians(theta)), 3)
h = im.height
yshift = abs(ct) * h
new_h = h + int(yshift)
affine = (1, 0, 0, ct, 1, -yshift if ct > 0 else 0)
# print("affine_tilt_vert ", affine)
return new_h, affine
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
new_h, affine = affine_tilt_vert(im, theta=-20)
im_new = im.transform((im.width, new_h), Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_tilt_vert.png")
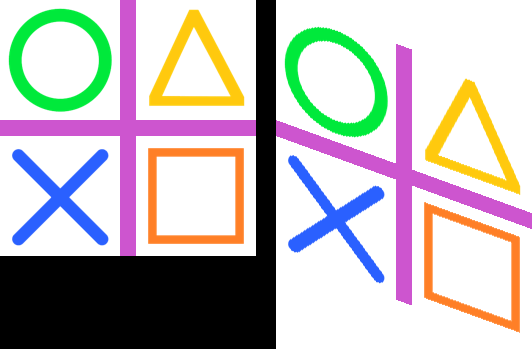
23.12. Transform.AFFINE rotate
from PIL import Image
def affine_rotation_coeffs(theta, x, y):
# affine formula to rotate theta about a point x, y
ct = math.cos(math.radians(theta))
st = math.sin(math.radians(theta))
return (ct, -st, x*(1-ct) + y*st, st, ct, y*(1-ct)-x*st)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
affine = affine_rotation_coeffs(theta=-10, x=128, y=128)
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.AFFINE, data=affine)
im_new.save("image/transform_affine_rotate.png")
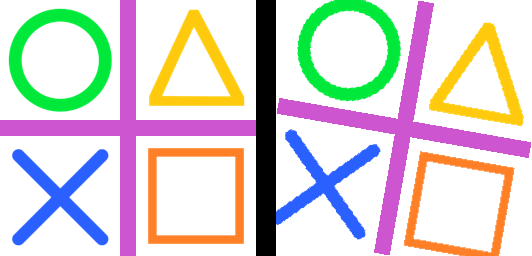
23.13. Transform.PERSPECTIVE
from PIL import Image
import math
def affine_rotation_coeffs(theta, x, y):
# affine formula to rotate theta about a point x, y
ct = math.cos(math.radians(theta))
st = math.sin(math.radians(theta))
return (ct, -st, x*(1-ct) + y*st, st, ct, y*(1-ct)-x*st)
with Image.open("test_images/shapes.png") as im:
perspective = (1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, -0.001, 0.001)
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE, data=perspective)
im_new.save("image/transform_perspective1.png")
perspective = (1, -0.364, 0, 0, 1, 0, -0.008, 0.001)
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE, data=perspective)
im_new.save("image/transform_perspective2.png")
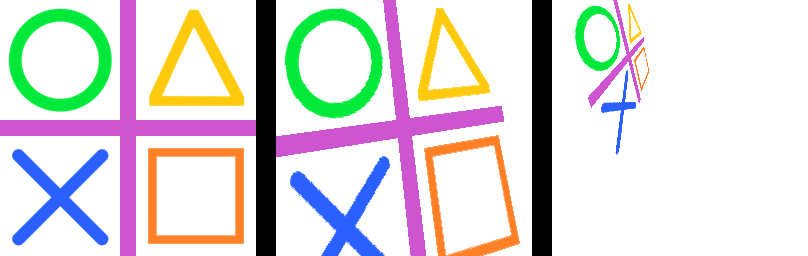
23.14. Transform.PERSPECTIVE coefficients
Below is a standard numpy function to calculate hte coefficients required for a perspective transform where the quad coordinates are given.
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
def find_coeffs(src, dst):
matrix = []
for (x, y), (X, Y) in zip(src, dst):
matrix.extend([
[x, y, 1, 0, 0, 0, -X * x, -X * y],
[0, 0, 0, x, y, 1, -Y * x, -Y * y],
])
A = np.matrix(matrix, dtype=float)
B = np.array(dst).reshape(8)
res = np.linalg.solve(A, B)
return np.round(np.array(res).reshape(8), decimals=4)
coeffs = find_coeffs(
[(0, 0), (93, 256), (256 + 93, 256), (256, 0)],
[(0, 0), (0, 256), (256, 256), (256, 0)]
)
# print(tuple(coeffs))
im_new = im.transform((256 + 93, 256), Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE, data=coeffs, resample=Image.Resampling.BICUBIC)
im_new.save("image/transform_perspective_coeff.png")
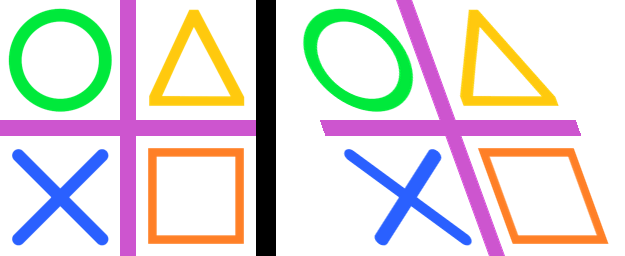
23.15. Transform.MESH
The code below has the same mesh classes as those in the ImageOps_deform section.
An example of a mesh form each deform class is shown below.
Cropping could be added to clip any black regions introduced by the deforms.
from PIL import Image, ImageOps
import math
class SingleDeformer:
def getmesh(self, img):
#Map a target rectangle onto a source quad
return [(
# target rectangle
(0, 0, 256, 256),
# corresponding source quadrilateral
(0, 0, 0, 256, 256, 256, 350, -100)
)]
class WaveDeformer:
def __init__(self, gridspace=20, sin_period_factor=40, x_dir=True, y_dir=True):
self.gridspace = gridspace
self.sin_amp = gridspace / 2
self.sin_period_factor = sin_period_factor
self.x_dir = x_dir
self.y_dir = y_dir
def transform_y(self, x, y):
y = y + self.sin_amp * math.sin(x / self.sin_period_factor)
return x, y
def transform_x(self, x, y):
x = x + self.sin_amp * math.sin(y / self.sin_period_factor)
return x, y
def transform_xy(self, x, y):
x = x + self.sin_amp * math.sin(y / self.sin_period_factor)
y = y + self.sin_amp * math.sin(x / self.sin_period_factor)
return x, y
def transform_rectangle(self, x0, y0, x1, y1):
if self.x_dir and self.y_dir:
return (*self.transform_xy(x0, y0),
*self.transform_xy(x0, y1),
*self.transform_xy(x1, y1),
*self.transform_xy(x1, y0),
)
elif self.x_dir:
return (*self.transform_x(x0, y0),
*self.transform_x(x0, y1),
*self.transform_x(x1, y1),
*self.transform_x(x1, y0),
)
elif self.y_dir:
return (*self.transform_y(x0, y0),
*self.transform_y(x0, y1),
*self.transform_y(x1, y1),
*self.transform_y(x1, y0),
)
else:
return (*self.transform_xy(x0, y0),
*self.transform_xy(x0, y1),
*self.transform_xy(x1, y1),
*self.transform_xy(x1, y0),
)
def getmesh(self, img):
self.w, self.h = img.size
self.gridspace
target_grid = []
for x in range(0, self.w, self.gridspace):
for y in range(0, self.h, self.gridspace):
target_grid.append((x, y, x + self.gridspace, y + self.gridspace))
source_grid = [self.transform_rectangle(*rect) for rect in target_grid]
return [t for t in zip(target_grid, source_grid)]
class BarrellDeformer:
def __init__(self, gridspace=10, k_1=0.2, k_2=0.05):
self.gridspace = gridspace
self.k_1 = k_1
self.k_2 = k_2
# adjust k_1 and k_2 to achieve the required distortion
def getmesh(self, img):
self.w, self.h = img.size
self.gridspace
target_grid = []
for x in range(0, self.w, self.gridspace):
for y in range(0, self.h, self.gridspace):
target_grid.append((x, y, x + self.gridspace, y + self.gridspace))
source_grid = [self.transform_rectangle(*rect) for rect in target_grid]
return [t for t in zip(target_grid, source_grid)]
def transform(self, x, y):
# center and scale the grid for radius calculation (distance from center of image)
x_c = self.w/2
y_c = self.h/2
x = (x - x_c) / x_c
y = (y - y_c) / y_c
radius = math.sqrt(x**2 + y**2) # distance from the center of image
m_r = 1 + self.k_1 * radius + self.k_2 * radius**2 # radial distortion model
# apply the model
x = x * m_r
y = y * m_r
# reverse the initial shifting
x = x * x_c + x_c
y = y * y_c + y_c
return x, y
def transform_rectangle(self, x0, y0, x1, y1):
return (*self.transform(x0, y0),
*self.transform(x0, y1),
*self.transform(x1, y1),
*self.transform(x1, y0),
)
with Image.open("test_images/cliffs.jpg") as im:
mesh_data = SingleDeformer().getmesh(im)
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.MESH, data=mesh_data)
# cropx, cropy = 32, 32
# box = (cropx, cropy, im.width - cropx, im.height - cropy)
# im_new = im_new.crop(box)
im_new.save("image/transform_mesh0.png")
mesh_data = WaveDeformer(gridspace=10, sin_period_factor=40, x_dir=True, y_dir=True).getmesh(im)
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.MESH, data=mesh_data)
# im_new.show()
im_new.save("image/transform_mesh1.png")
mesh_data = BarrellDeformer(gridspace=20, k_1=0.2, k_2=0.05).getmesh(im)
im_new = im.transform((256, 256), Image.Transform.MESH, data=mesh_data)
# im_new.show()
im_new.save("image/transform_mesh2.png")
